Click below to listen to my 2 min. Garden Bite radio show: What the heck is mycorrhizae?
It’s the fungi with the funny name. Mycorrhizae fungi have a symbiotic relationship with the roots of many plants. Mycorrhizae play an important role in plant nutrition.

The fungus, because it does not photosynthesize, cannot fix its own carbon. Consequently, it receives all of its necessary carbohydrates from the host plant. In return, the mycorrhiza absorbs nutrients from the soil which are passed along to the plant. Cool, huh!

In most situations, the roots of a plant occupy only 0.5% of the topsoil volume and even less of the subsoil. But mycorrhizae can reach much deeper allowing those nutrients to pass on to the roots of your plants.
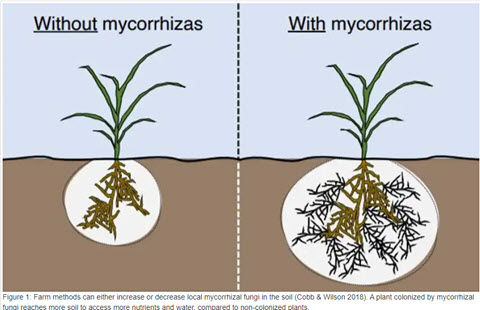
The University of Wisconsin Extension says in addition to increasing the uptake of nutrients, mycorrhizae often provide some protection against soil-borne diseases. They may also increase a plant’s tolerance to adverse conditions. Drought, high temperatures, salinity, and acidity, or a build-up of toxic elements in the soil are some of the effects on host plants that mycorrhizae reduce. This aspect may be important to a tree’s survival in landscape plantings.
Think about my lawn watering tips from yesterday! Adding mycorrhizae may have helped in this extensive heat wave.

Many local garden centers sell this amazing fungi. Check the package to make sure it contains mycorrhizae aka mycorrhizal ….

Can you add too much? Yes, read on for more information.
Resources:
- University of Minnesota Extension
- University of Wisconsin Extension
- Mother Earth News – Mycorrhizal fungi
